Advances in breast surgery help optimize cancer outcomes while minimizing side effects. Several innovative techniques are now used to provide a more targeted, less invasive, and better-tolerated approach:
Endoscopic breast surgery
Endoscopic breast surgery is a less invasive alternative to traditional open surgery. It is used for procedures such as breast augmentation, reconstruction after cancer, and certain prophylactic mastectomies.
A small camera inserted through a tiny incision provides the surgeon with a clear view of the tissues, allowing for precise dissection and preservation of surrounding structures. This minimally invasive approach reduces visible scars, limits post-operative pain, and speeds up recovery.
In the case of mastectomy, it enables accurate removal of breast tissue and often facilitates immediate reconstruction using implants or autologous tissue.
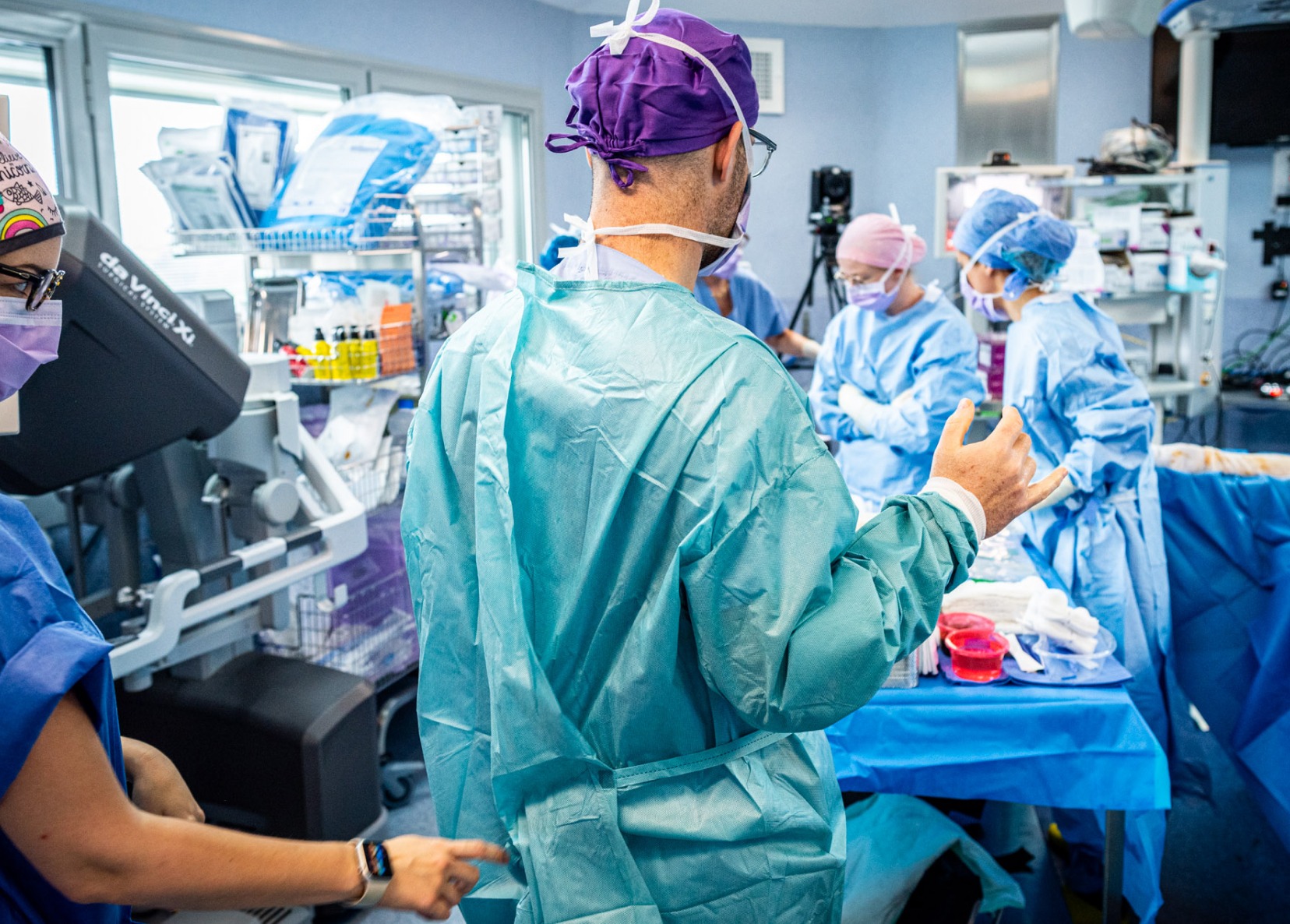
Robotic surgery
Robot-assisted breast surgery is a major breakthrough in the field. With advanced technology, it allows for highly precise interventions, resulting in smaller scars and improved aesthetic outcomes. It is used for breast reconstruction, lumpectomies, and prophylactic surgery in high-risk patients.
By precisely targeting affected tissues, robotic surgery preserves surrounding anatomy and improves oncological outcomes. The surgeon operates remotely using a console, with 3D high-definition vision, reducing complications and accelerating recovery.
Local anesthesia
Local anesthesia offers an effective alternative to general anesthesia for selected breast procedures. It helps avoid systemic side effects, shortens hospital stays, and promotes faster return to normal activities.
This method is particularly suited to minimally invasive, outpatient surgeries.
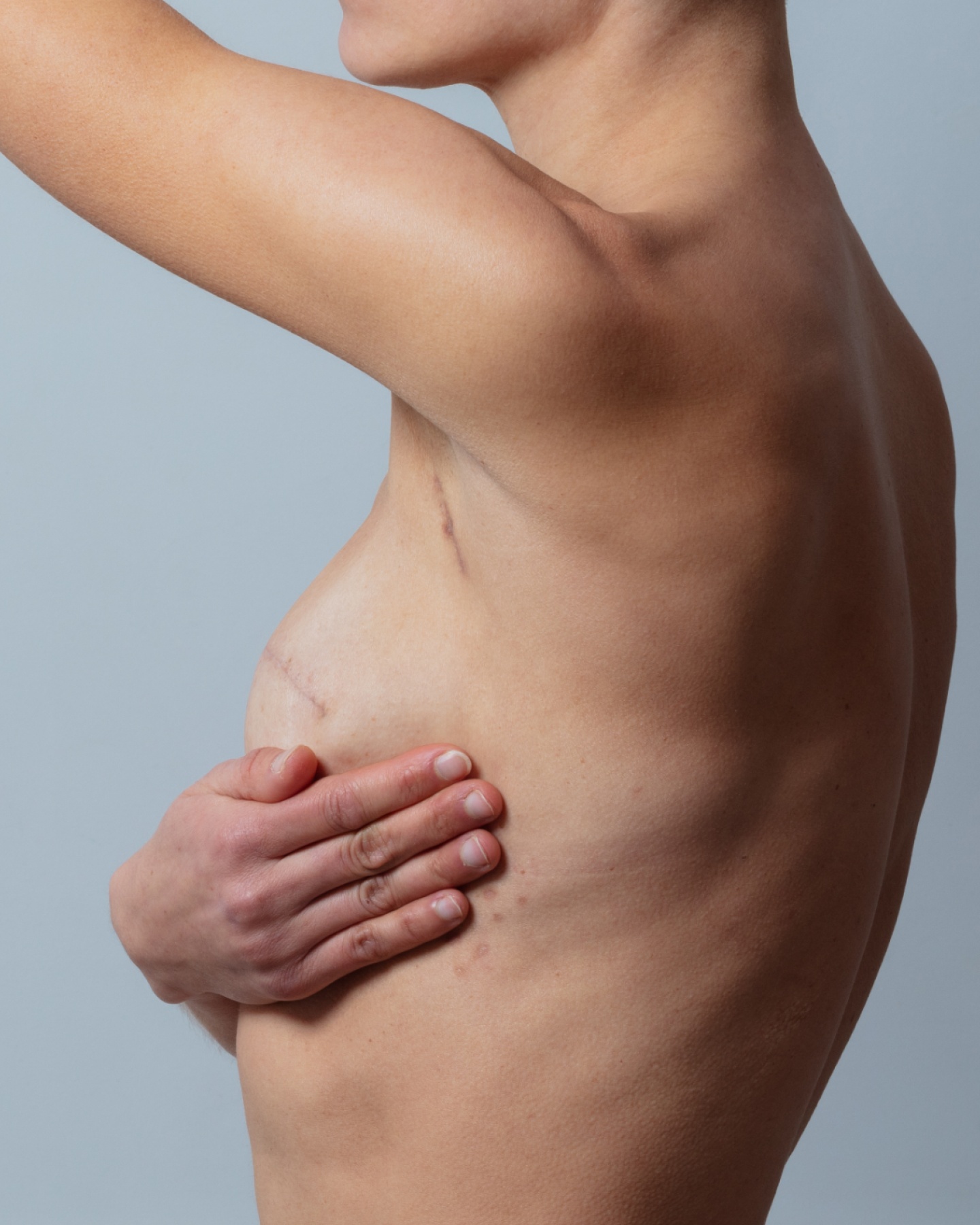
Pre-pectoral breast reconstruction
Following a mastectomy, breast reconstruction can be performed immediately or at a later stage. The pre-pectoral technique involves placing the implant above the pectoral muscle, rather than beneath it. This avoids pain linked to muscle dissection and offers a more natural result.
Using biological matrices improves implant tolerance and aesthetic outcomes. When possible, nipple preservation is combined with this method to enhance final results.
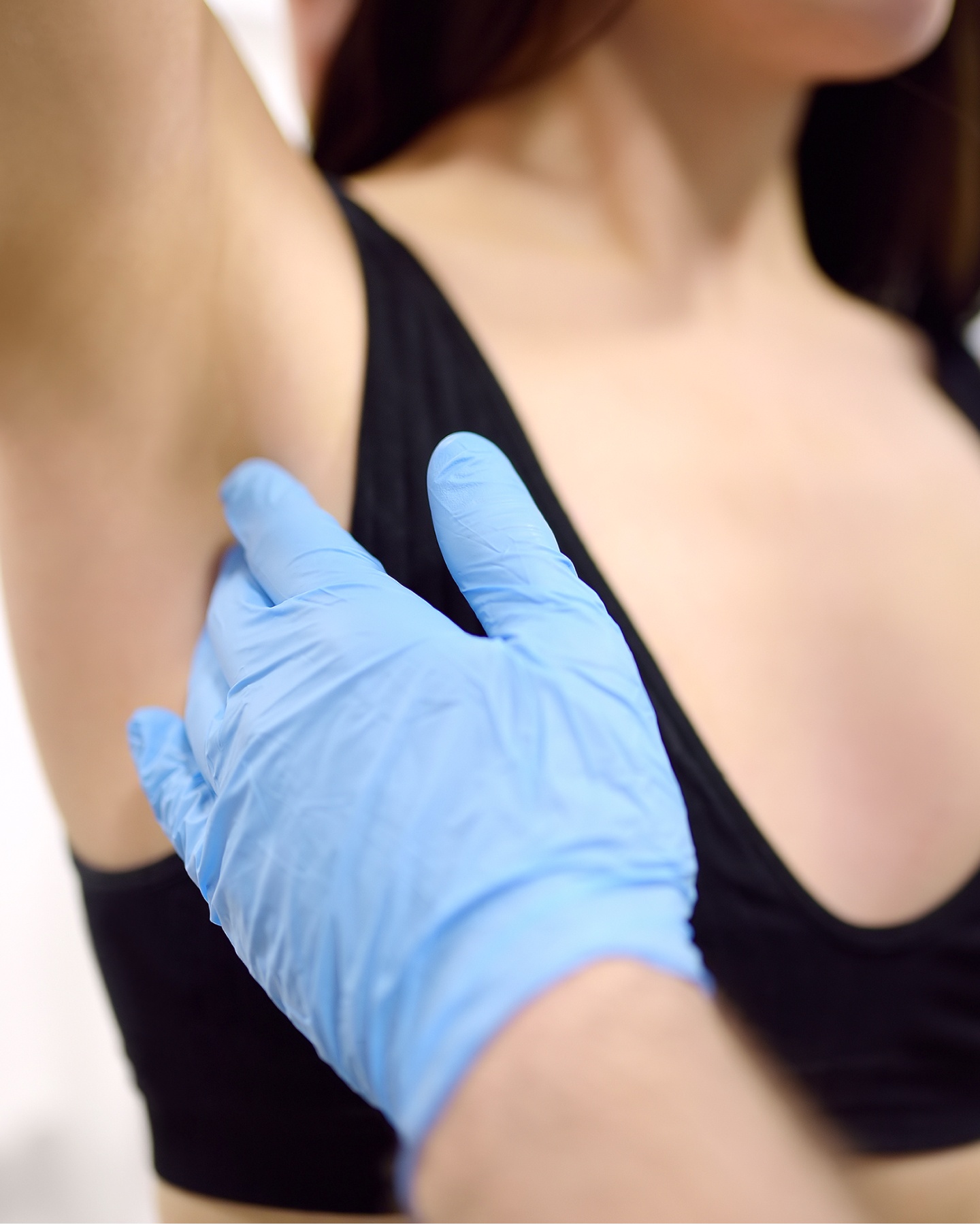
Minimally invasive lymph node surgery
Lymph node evaluation is crucial in assessing breast cancer spread. The sentinel lymph node technique targets the first nodes draining the tumor, helping avoid full lymph node dissection when unnecessary.
This reduces complications such as lymphedema (arm swelling) and limits long-term functional effects.
Minimally invasive localization
To enhance surgical precision, minimally invasive localization techniques are performed before surgery. Metallic clip placement helps accurately identify the tumor or suspicious lymph nodes, guiding the surgeon for a targeted excision.
These innovations reduce the margin of error and improve outcomes in conservative surgery.